We use commercial and our own software developed for numerical simulations.
Commercial software
3D modeling
2D modeling
1D modeling:
In addition, we use the following software for our activity:
- AutoCAD – Civil3D, Map, 3DS Max Design
- ArcGIS
- AtlasDMT
- BASEGRAIN
- Hydro
- MATLAB
- R
- STATISTICA
- Surfer
- Tecplot
Software developed by us
Shore
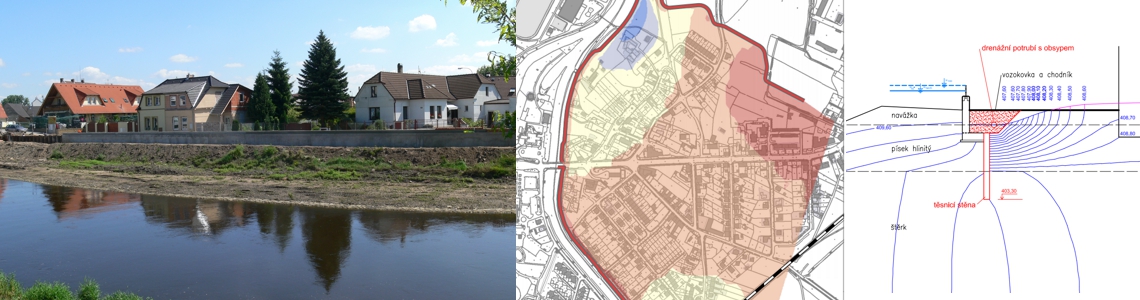
Manual, templates, and tools for creating Shoreline Hazards from Wind Oscillation Waves maps – designed for ArcGIS PRO 2.X enviroment. Output from the project TH03030182 “Protection of water structures and natural banks from the effects of oscillating wind waves.”
HPV
Software for evaluating the flow of groundwater with free water level in the zone at the boundary of the saturated and unsaturated layers and for determining seepage areas.
HPV-1D
HPV-1D enables 1D calculations of the flow of groundwater with free and confined water levels through isotropic and anisotropic media composed of more materials.
HPV-2D
HPV-2D enables 2D calculations of the flow of groundwater with free and confined water levels in horizontal and vertical planes through isotropic and anisotropic media composed of more materials.
KMH
Software for calculating control limit levels at water-retaining structures as part of the evaluation of their reliability and stability.
NATRZ
This program is created for use in solving failures of embankment dams due to overtopping.
NEST
The program for calculating 1D steady-state non-uniform flow in open channels.
Levee optimization
Template for creating maps for levee optimization – designed for ArcGIS PRO 2.X environment. Output from the the project TH04030087 “Tools for optimization of levee system management”
PV_OPTIM
This software is made for optimising the half-band width of the matrix for groundwater programs.
VSAK 1.0
The software VSAK 1.0 contains modules for evaluating the coefficient of seepage, hydraulic conductivity, the coefficient of uncertainties in seepage and the design of the retention water capacity of infiltration facilities.
Vyvar
The program solves the design of the stilling basin below a water structure. The calculation itself lies in the determination of depths of water in the supply channel and in the tail race and the energy overflow head. Then, mutual depths are determined, as well as the position of the hydraulic jump in relation to the structure. Subsequently, the calculation of the dimension of the stilling pool is finished, i.e. its recess and its length.
ZScan
The user program of the Z-meter device.
Ztraty
The extension of the ArcGIS software created in the Visual Basic language serves for estimates of the potential loss of human life during flood events.